Gavi
Antibiotics are drugs designed to treat infections caused by bacteria (for example, skin infections). They don’t work on infections caused by other microbes such as viruses (including COVID and flu) or fungi.
Gavi
Scientists are trying to find out whether there’s a genetic reason certain people have managed to avoid COVID
Nature
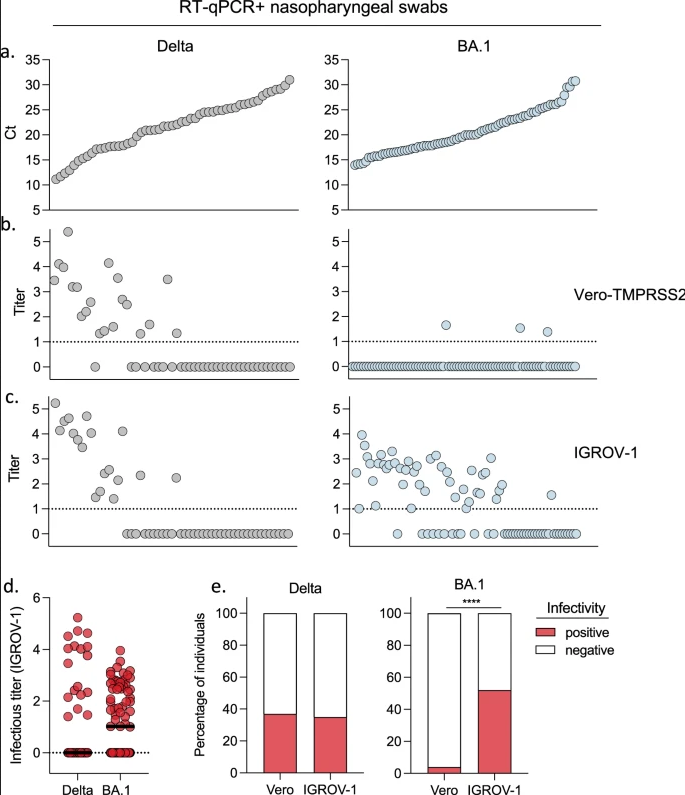
Convergent evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2, BA.4, and BA.5 lineages has led to the emergence of several new subvariants, including BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6. and BQ.1.1.
PubMed
It has been shown that stimulation of innate immunity may provide temporary protection against a variety of infectious diseases.
News Medical
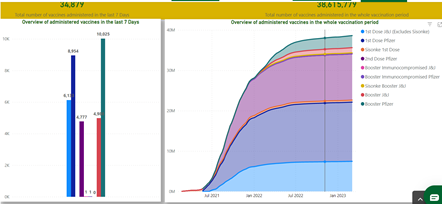
In many African countries, COVID-19 vaccine coverage remained significantly slow for a prolonged period, primarily due to vaccine shortage.
World Bank
The COVID-19 Vaccine Survey (CVACS) is a South African national panel study of individuals initially...
News Medical
Variable recovery duration and a variety of problems have been among the many debatable elements of COVID-19 experienced by numerous individuals.
Edin. University
The higher prevalence of common cold viruses in Africa may have helped the continent experience relatively lower death rates from Covid-19, a study of people in Zimbabwe suggests.
News Medical
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infections, related hospitalizations, and deaths has been critical for ...
LSHTD
What we can learn from the history of vaccine science and development.